2) OOPs allows to decompose the problem into a number of entities called object and then design data and functions around these entities.
Characteristics of OOPs
1) Emphasis is on data.
2) Large problems is divided into what are known as object.
3) Function that operate on the data of an object are tied together in a data structure.
4) Data structures are design such that they characterized the problem well.
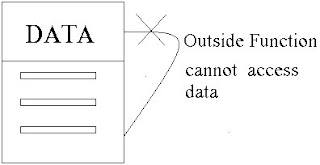
5) Data is hidden & cannot be accessed directly by outside functions.
6) New data & Functions can be accommodated easily & effectively.
7) Employs Bottom-Top approach in program design.
Elements of Object Oriented Programming
Characteristics of OOPs
1) Emphasis is on data.
2) Large problems is divided into what are known as object.
3) Function that operate on the data of an object are tied together in a data structure.
4) Data structures are design such that they characterized the problem well.
5) Data is hidden & cannot be accessed directly by outside functions.
6) New data & Functions can be accommodated easily & effectively.
7) Employs Bottom-Top approach in program design.
Elements of Object Oriented Programming
Class Inheritance Object
Polymorphism Data Encapsulation
Dynamic Binding Data Abstraction Message Communication
1) Class:- Class specifies the criteria to handle the instance of the problem. Class is a user define data type. The entire set of data and functions(Methods) associated with the problem can be bound together & implemented as a type using class.
2) Object:- Object is an instance of the class. Infact, object are variables of type class.
Objects are basic run time entities in an Object oriented system.
3) Data Encapsulation:- The wrapping up of data and functions together into a single unit (Called Class) is known as Data Encapsulation.
Through Data Encapsulation, the data is not accessible directly to outside functions, and only the functions that are wrapped i nside the class can access them.
This insulation of data from dire ct access by outside functions is called " DATA HIDING".
Since class user the concept of Data Abstraction, it is also known as Abstract Data Type "ADT".
5) Inheritance:-Inheritance is the process by which an objct of one class requires the properties of another class.It supports the concept of Hierarcical classsifiction. In Object Oriented Programming the concept of i nheritance provides the idea of reusability.
6) Polymorphism [Poly (Many) +Morphing (Forms)]:-
For example :- An operator may exhibit different behaviour in different situations.
In Object Oriented Programming, polymorphism plays an important role allowing objects having different internal structur es to share the same external interface.
The most important advantage of polymorphism is that it allows to identity the process by its natural name.
7) Dynamic Binding:-
Binding refers to the act of linking of procedure (function) called statement to the function code to be executed in response to the call.
Dynamic Binding means that the function code to be executed is response to particular call is not known until at the time of call during program execution.
8) Message Communication:
Objects are basic run time entities in an Object oriented system.
3) Data Encapsulation:- The wrapping up of data and functions together into a single unit (Called Class) is known as Data Encapsulation.
Through Data Encapsulation, the data is not accessible directly to outside functions, and only the functions that are wrapped i nside the class can access them.
This insulation of data from dire ct access by outside functions is called " DATA HIDING".
4) Data Abstraction:- Abstraction refers to reprenting essential features without specifing backgroung details and explanations.
Since class user the concept of Data Abstraction, it is also known as Abstract Data Type "ADT".
5) Inheritance:-Inheritance is the process by which an objct of one class requires the properties of another class.It supports the concept of Hierarcical classsifiction. In Object Oriented Programming the concept of i nheritance provides the idea of reusability.
6) Polymorphism [Poly (Many) +Morphing (Forms)]:-
Operator Polymorphism Function polymorphism n1 + n2 add two integers sort(arr,10); Single Function m1 + m2 add two matrixs sort(matrix); Doing s1 + s2 add two objects sort(str,10); Many tasksPoly morphism is an important Object Oriented Programing concept, polymorphism means the ability to take different forms.
For example :- An operator may exhibit different behaviour in different situations.
In Object Oriented Programming, polymorphism plays an important role allowing objects having different internal structur es to share the same external interface.
The most important advantage of polymorphism is that it allows to identity the process by its natural name.
7) Dynamic Binding:-
Binding refers to the act of linking of procedure (function) called statement to the function code to be executed in response to the call.
Dynamic Binding means that the function code to be executed is response to particular call is not known until at the time of call during program execution.
8) Message Communication:
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed